Generative AI represents one of the most transformative technological developments of our time. Unlike traditional AI systems that analyze or classify existing data, generative AI creates new content that never existed before. This new content ranges from text and images to music and code.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI refers to artificial intelligence systems. These systems are designed to produce content based on patterns learned from vast amounts of training data. These systems use sophisticated neural network architectures, particularly transformer models, to understand the underlying structure and relationships within data.
The technology works by predicting what comes next in a sequence. This could be the next word in a sentence, a pixel in an image, or a note in a musical composition. Through extensive training on diverse datasets, these models develop a nuanced understanding of language, visual concepts, or other patterns.
Foundation Models (FMs) and Their Differences from Traditional Models
Foundation models (FMs) are large pre-trained models that serve as a starting point for developing more specialized AI applications. They represent a significant evolution in machine learning architecture and capabilities.
What are Foundation Models?
Foundation models are large-scale AI models that have been trained on massive datasets, often containing text, images, or other modalities. These models learn general patterns and representations from this data. This allows them to be adaptable to many downstream tasks without requiring complete retraining.
A foundation model is “a large pre-trained model.” It is adaptable to many downstream tasks. It often serves as the starting point for developing more specialized models. Examples include models like Llama-3-70b, BLOOM 176B, Claude, and GPT variants.
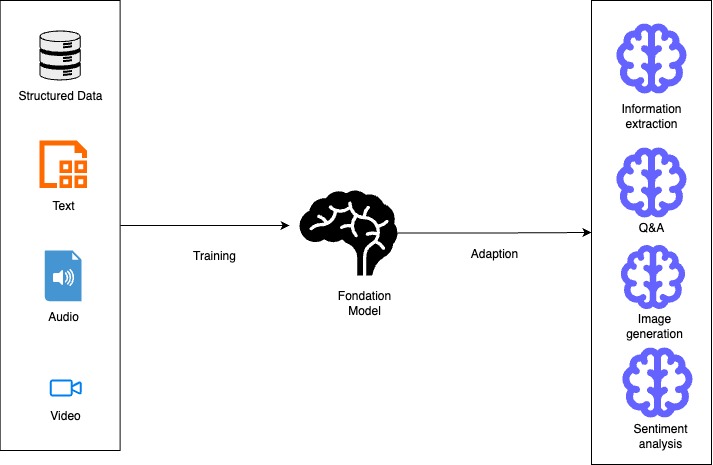
Key Differences from Traditional Models
1. Training Approach
- Foundation Models: These are pre-trained on vast, diverse datasets. They use a self-supervised or semi-supervised manner. This method allows them to learn patterns and representations without explicit labels for specific tasks.
- Traditional Models: Typically trained from scratch for specific tasks using labeled datasets designed for those particular applications.
2. Scale and Architecture
- Foundation Models: Enormous in size, often with billions or trillions of parameters. For example, Claude 3 Opus and Llama-3-70B have tens or hundreds of billions of parameters.
- Traditional Models: Generally much smaller. They have parameters ranging from thousands to millions. These models are designed with specific architectures. They are optimized for particular tasks.
3. Adaptability and Transfer
- Foundation Models: Can be adapted to multiple downstream tasks through fine-tuning, prompt engineering, or few-shot learning with minimal additional training.
- Traditional Models: Built for specific applications and typically require complete retraining to be applied to new tasks.
4. Resource Requirements
- Foundation Models: Require significant computational resources for training and often for inference, though smaller variants are being developed.
- Traditional Models: Can often run on less powerful hardware, making them more accessible for deployment in resource-constrained environments.
5. Data Requirements
- Foundation Models: Require massive datasets for pre-training but can then generalize to new tasks with relatively little task-specific data.
- Traditional Models: Require substantial task-specific labeled data to achieve good performance.
6. Capabilities
- Foundation Models: They can generate human-like text. They understand context across long sequences. They create images from text descriptions. They also demonstrate emergent abilities not explicitly trained for.
- Traditional Models: Usually perform a single task or related set of tasks. Their capabilities are limited to what they were explicitly trained to do.
Foundation Models in AWS
AWS offers foundation models through services like:
- Amazon Bedrock: A fully managed service providing access to foundation models from providers like Anthropic, Cohere, AI21 Labs, Meta, and Amazon’s own Titan models.
- Amazon SageMaker JumpStart: Offers a broad range of foundation models that can be easily deployed and fine-tuned, including publicly available models and proprietary options.
Foundation models in these services can be used for various generative AI applications including content writing, code generation, question answering, summarization, classification, and image creation.
Amazon Bedrock
Amazon Bedrock is a fully managed service. It offers a simple way to build and scale generative AI applications. These applications use foundation models (FMs). Here’s how you can leverage it:
- Access to Multiple Foundation Models
Amazon Bedrock offers unified API access to various high-performing foundation models. These models come from leading AI companies such as Anthropic, Cohere, Meta, Mistral AI, AI21 Labs, Stability AI, and Amazon. This allows you to experiment with different models and choose the best one for your specific use case without committing to a single provider.
- Building Applications
You can build applications using the AWS SDK for Python (Boto3) to programmatically interact with foundation models. This involves setting up the Boto3 client, defining the model ID, preparing your input prompt, creating a request payload, and invoking the Amazon Bedrock model.
- Key Features and Capabilities
- Model Customization: Fine-tune models with your data for specific use cases
- Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG): Enhance model responses by retrieving relevant information from your proprietary data sources
- Agent Creation: Build autonomous agents that can perform complex tasks using the AWS CLI or CloudFormation
- Knowledge Bases: Query your data and generate AI-powered responses using the
retrieve-and-generatefunctionality - Guardrails: Implement safeguards based on your use cases and responsible AI policies
- Security and Privacy
Bedrock provides robust security features, including data protection measures that don’t store or log user prompts and completions. You can encrypt guardrails with customer managed keys and restrict access with least privilege IAM permissions.
- Deployment Options
- On-demand: Pay-as-you-go model invocation
- Cross-Region inference: Enhance availability and throughput across multiple regions
- Provisioned throughput: Reserve dedicated capacity for consistent performance
- Integration with AWS Ecosystem
Amazon Bedrock seamlessly integrates with other AWS services, making it easy to build comprehensive AI solutions. You can use SageMaker ML features for testing different models and managing foundation models at scale.
By leveraging Amazon Bedrock, you can quickly build and deploy generative AI applications. You can maintain security, privacy, and responsible AI practices. All this is achieved without having to manage complex infrastructure.
The Future Landscape
Generative AI will continue evolving rapidly, with improvements in reasoning ability, multimodal capabilities, and specialized domain expertise. Organizations that thoughtfully integrate these technologies will likely gain significant competitive advantages in efficiency, creativity, and problem-solving.
Key Applications of Generative AI
Generative AI is already transforming numerous fields:
- Content Creation: Generating articles, marketing copy, and creative writing
- Visual Arts: Creating images, artwork, and designs from text descriptions
- Software Development: Assisting with code generation and debugging
- Customer Service: Powering intelligent virtual assistants and chatbots
- Healthcare: Aiding in drug discovery and personalized treatment plans
- Manufacturing: Optimizing product design and production processes
References:
- Build generative AI applications on Amazon Bedrock with the AWS SDK for Python (Boto3)
- Generative AI for the AWS SRA
- Build generative AI solutions with Amazon Bedrock
- Choosing a generative AI service
- Amazon Bedrock or Amazon SageMaker AI?
- Amazon SageMaker JumpStart Foundation Models
- Amazon Bedrock or Amazon SageMaker AI?
- Amazon Bedrock Models