Migration to cloud for an enterprise is a journey rather than one stop destination. This journey has mainly following stops
- Rehost– This is the easiest way to migrate to cloud. But using this way you cannot take most of the advantages the cloud offers like Cost, Availability, Scalability, Performance etc.
- Refactor– When the application is re-factored to the minimum extent to be migrated to Platform-as-a-Service or managed services. This includes removing any hardware or 3rd party dependencies, refactoring the logging and caching strategy etc.
- Re-architect– When the app is completely re-architectured to a cloud native, serverless or microservice based architecture to move from its legacy architecture. Even though it maybe the ultimate destination for an organization but it is extremely expensive and time consuming.
As we discussed above, this journey to cloud is an continuous one. The organization should go with a phased approach rather than going for bing bang re-architecture approach taking a balanced approach.
background
In this article we will discuss journey to cloud for an imaginary company ABC Inc. The ABC Inc. is the major telecommunication company of the country. It has strong local presence with global ambitions. We are helping them in devising the road-map for their strategic Journey to Cloud initiative. The Rehost is out of scope as the customer doesn’t want to go with this approach. The ABC Inc. would like to migrate their online customer portal to cloud that allows customers to check their account, change plans, monitor usage and pay bills. The primary driver for the migration is to address the recent performance issues at peak load.
Current State
The customer portal is a 2-tier app with front-end built in Java Servlets and JSP with back end as Oracle database, the app integrates with Billing app using IBM MQ, Reward Platform over SOAP service and Payment System using Java RMI. Below is the logical representation of the architecture-

solution
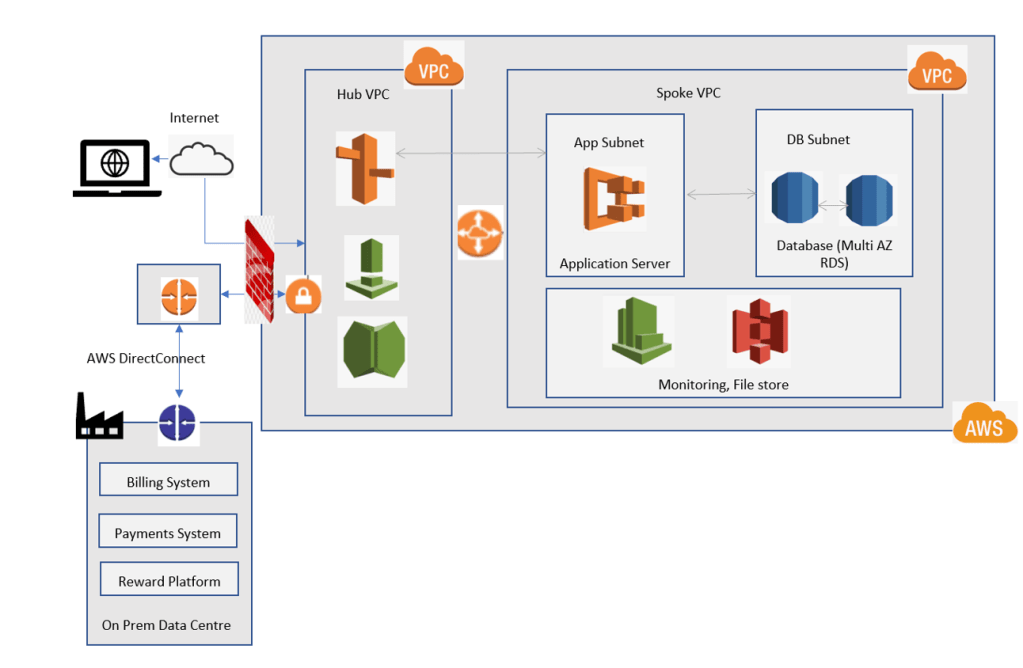
- Immediate Goal: Refactor to adapt to cloud native architecture: Moderate code change effort- The step 1 is to refactor the app to host in AWS using its native services.
- Front End Layer– The front end of the app will be containerized to be hosted on AWS ECS. Using ECS, that is a fully managed container service to deploy, manage and orchestrate the containerized apps, we modernize the app to a certain extent, also there is no need to manage the control plane or nodes per se, exploiting the benefit of cloud based managed services to the maximum.
- DB Layer– The Oracle database is hosted in AWS RDS instance. RDS is also a fully managed RDBMS service by AWS. AWS provides tools like AWS Data Migration Service to migrate the data in real time to RDS. RDS is setup with Multi AZ deployment for HA and cross region Read replica for DR.
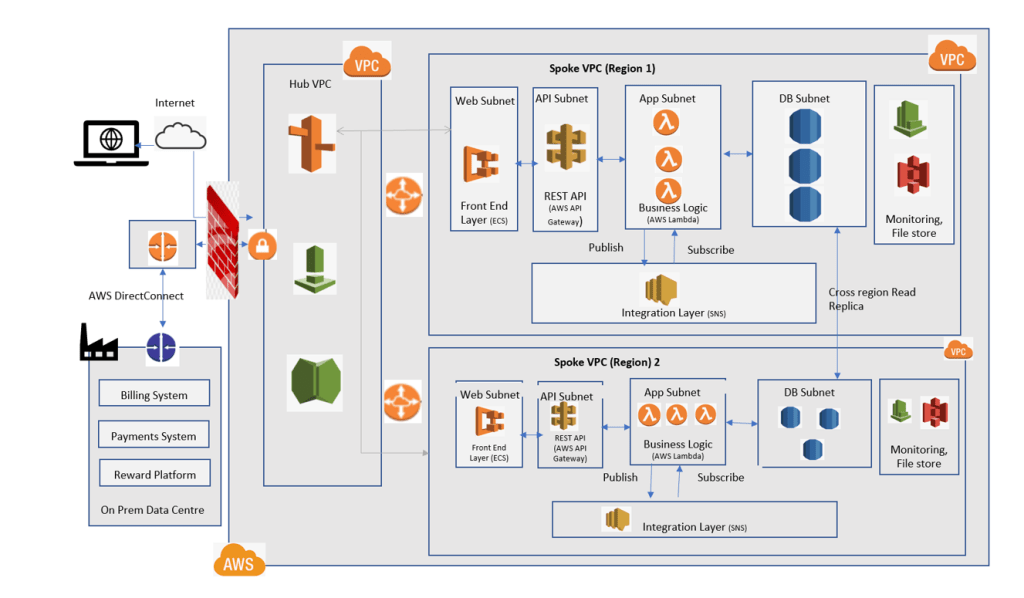
2. End Goal: Modernise the app to microservice based architecture: Significant code change effort- The end state is to refactor and modernize the monolithic architecture to serverless microservice based architecture.
- Front End Layer– The front end of the app will be containerized to be hosted on AWS ECS.
- REST Layer– The REST layer will host a REST API that is deployed on a AWS API Gateway, which is a serverless component from AWS that acts as a front door for the app.
- Business Logic Layer– This layer contains actual busines logic. The single large monolith service will be broken into smaller, relatively logically independent, services like User Management Service, Payment Service, Monitor Usage service and will be written and deployed using AWS Lambda, those are also serverless components that allows to write and run code without the hassle of provisioning or managing the infrastructure.
- Integration Layer– This is a pub/sub event-based integration layer implemented using AWS Simple Notification Service (SNS), that provides topics for high throughput, push based many to many messaging-based event-driven architecture. The layer will be used to maintain the consistency among the databases related to different services. The service will perform a task and publish an event to SNS with the required data and the subscribers (other services) will get triggered and take action according to the event and update the corresponding data in the database.
- DB Layer– The Oracle database is hosted in AWS RDS instance. RDS is also a fully managed RDBMS service by AWS. AWS provides tools like AWS Data Migration Service to migrate the data in real time to RDS. Each service will have its own database, thus improving the overall performance. The RDS will be setup for Multi AZ deployment for HA and cross region Read replica for DR.

- Future Enhancements- Global Road-map- With ABC Inc. having global aspirations, the solution can be hosted as a multi-region solution, the AWS Route 53 will use — based routing to route the request nearest available region to the end customer, hence providing the consistent user experience across the globe.
Conclusion
As we see here, the journey to cloud program for the customer portal for ABC Inc is carried out in 2 steps-
- Refactor the app to move to AWS native architecture
- Modernize the app to microservice based architecture with the ability for further extension to fulfil its global aspirations.